This Slovin’s formula calculator computes the minimum number of samples needed from a population to meet your desired statistical accuracy using Slovin’s formula. It also provides a step-by-step explanation showing exactly how the sample size was calculated, so you can easily understand and verify the results.
Simply enter your population size and margin of error as a decimal to calculate the required sample size using Slovin’s formula.
How to Use the Slovin’s Formula Calculator
Using this calculator is fast and easy. Just follow these steps:
- Enter the population size (N): The total number of individuals in your population.
- Enter the margin of error (e): For example, 0.05 for 5% or 0.01 for 1%.
- Click Calculate: The tool uses Slovin’s formula to compute your sample size instantly.
The calculator provides you with the minimum sample size along with a step-by-step explanation of how to compute the sample size manually.
What is Slovin’s Formula?
Slovin’s formula is a simple mathematical formula used to calculate the sample size needed from a given population. It is ideal when you know the total population but it is not realistic to include everyone in a study. Instead of surveying the entire population, Slovin’s formula helps researchers determine the minimum number of respondents required to achieve reliable results.
The formula was introduced by Slovin in 1960 and has since become a common method for sample size determination in academic and professional research. The formula is:
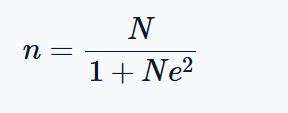
Where:
- n is the required sample size
- N is the total population size
- e is the margin of error
When to Use Slovin’s Formula?
Knowing when to use Slovin’s formula is important for applying it correctly in research. This formula is especially useful when you have a known population size but cannot survey every individual. Some of the common situations where you can use the formula include:
- Surveys and questionnaires: For example, when researchers want to collect opinions from a large group but need only a representative sample.
- Population studies: When studying communities, schools, or organizations where the total number of members is already known.
- Academic research projects: Students often use Slovin’s formula to quickly estimate sample size for theses and dissertations.
However, Slovin’s sample size formula is associated with a number of limitations, which include:
- It works best as a quick estimation method rather than a precise statistical tool.
- It assumes random sampling, which may not always be possible in real-world studies.
- It does not consider population variability or standard deviation.
Sample Size Calculation Using Slovin’s Formula: Solved Example
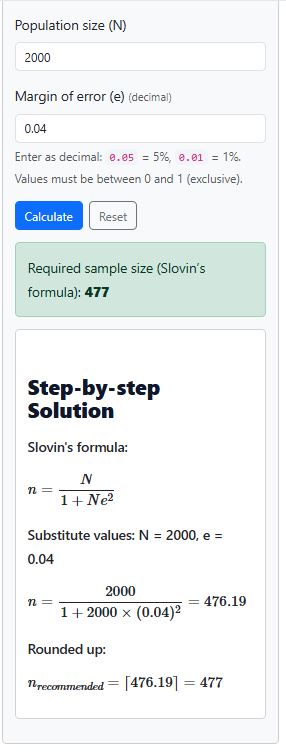
Imagine you are conducting a survey in a town with 2,000 residents, and you want to know people’s opinions about a new community project. Since it is not realistic to ask every resident, you decide to use Slovin’s formula to find the right sample size. You also choose a margin of error of 4% (0.04) to keep results accurate. Calculate the appropriate sample size to sample.
Solution:
- Step 1: Write the formula: $$n = \frac{N}{1 + Ne^{2}}$$
- Step 2: Substitute the numbers: $$n = \frac{2000}{1 + 2000(0.04)^{2}}$$
- Step 3: Finish the division: $$n = \frac{2000}{4.2} = 476.19$$
- Step 4: Round up to a whole number. Thus, the required sample size is 477 respondents.
Alternatively, using the Slovin’s formula calculator and specifying the population and margin of error, you get instant and accurate results as shown below:
Frequently Asked Questions
Slovin’s formula is a statistical method used to determine the minimum sample size needed from a population. It ensures that your survey or study results are accurate while keeping the sample size manageable.
The Slovin’s sample size calculator quickly computes the number of samples required for a given population. By entering your population size and margin of error, it provides the minimum sample size along with a clear step-by-step calculation using Slovin’s formula.
You should use Slovin’s formula when the population size is known, random sampling is possible, and you want a quick estimate of the sample size. It is most common in surveys, academic research, and basic population studies.
The slovin’s sample size formula is: n= N / (1+N*e^2)
Where:
– n is the required sample size
– N is the total population, and
– e is the margin of error.
The calculator automatically applies this formula for accurate results.
Common choices are 5% (0.05) or 1% (0.01), depending on how precise you want your results. A smaller margin of error requires a larger sample size.
Slovin’s formula is simpler and used for quick estimates when the population size is known. On the other hand, Cochran’s formula is more advanced and takes variability into account, making it better for detailed research.