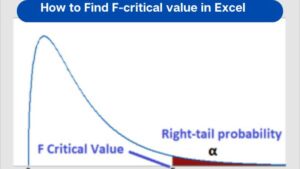
After performing an F-test for ANOVA, equality of variance test, or a regression model, you obtain an F-test statistic. The next step involves finding an F-critical value to help you determine whether the results are statistically significant or not. There are various methods for finding F-critical values. The classical approach involves reading critical values from f-tables. However, for quick and accurate solutions, an online f-critical value calculator or Excel function can be very helpful. In this article, you’ll learn how to find the f critical value using the Excel function (with worked out example).
Key TakeAways
- The F.INV.RT() function makes it easy to find the F critical value using Excel.
- To find the critical value, type
=F.INV.RT(alpha, df1, df2)in a cell where you want the critical value to appear. You should replace alpha, df1, and df2 with actual values. - Once you click the Enter key on the keyboard, Excel will return the right-tailed F-critical value.
- Most tests, such as ANOVA, F-tests for equality of variance, and regression analysis requires the right-tailed F critical value.
- The Decision is to reject the null hypothesis if the F-test statistic is greater than the critical F value. Otherwise, you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
How to Find the F Critical Value in Excel
To find the F-critical value in Excel, we use the F.INV.RT() function. The function accepts three key parameters, which include:
- Significance level, α
- The numerator degrees of freedom, df1
- The denominator degrees of freedom, df2
With the three parameters, you can easily find the F critical value using the formula =F.INV.RT(α, df1, df2). Therefore, to find the critical F value using Excel, follow these steps:
- Open a blank Excel sheet
- In a cell where you want the F-critical value to appear, type the formula
=F.INV.RT(alpha, df1, df2). (You should replace alpha, df1, and df2 with your actual values) - Press the Enter key.
Excel will instantly return the correct critical value for your F test.
Finding the F-Critical Value Using Excel: Example
Imagine you want to compare the variance of two production lines in a factory. You plan to run an F-test to see if the variability in output is different between the two lines. Assuming a 5% significance level, 4 numerator degrees of freedom, and 10 denominator degrees of freedom, find the appropriate F critical value for this test.
Solution
From the scenario, we can identify the three parameters as follows:
- Significance level, α = 5% = 0.05
- The numerator degrees of freedom are 4
- The denominator degrees of freedom are 10
Therefore, to find the F-critical value for the test using the F.INV.RT() function, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Open a Blank Excel sheet
- Step 2: In a cell where you want the critical value to appear, type the formula:
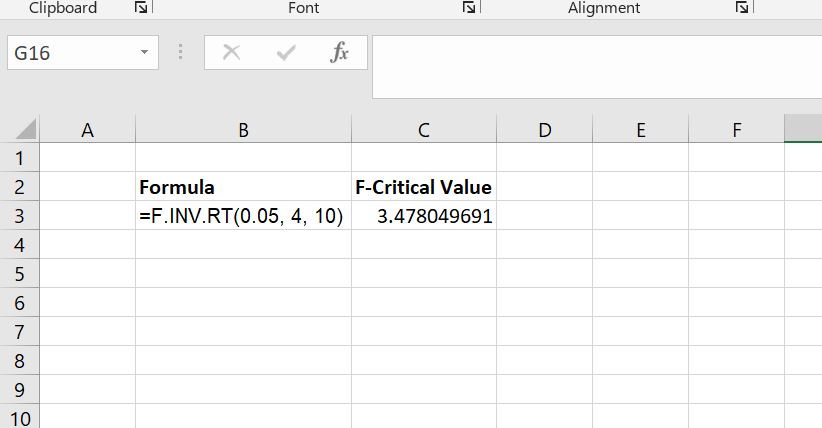
=F.INV.RT(0.05, 4, 10) - Step 3: Press the Enter key
The Excel formula will return the correct critical value for the test as 3.4780 (see Figure 1).
Note. You can also confirm the value using the F distribution table. In this case, you need to look up the f-table with alpha = 0.05 and look for the intersection of df1 = 4 and df2 = 10.
Quick Tips
Here are a few tips to keep in mind to avoid mistakes when calculating critical F values in Excel:
- Double-check your degrees of freedom. Make sure the numerator (df1) and denominator (df2) are correct. Reversing them will give the wrong value.
- Use the correct significance level. Common choices are 0.01, 0.05, or 0.10. Enter it as a decimal, like 0.05.
- Always use F.INV.RT. This function gives the right-tail F-critical value. Avoid using older functions like FDIST unless you are using legacy Excel versions.
- Ensure no extra spaces or errors in the formula. Even small mistakes in typing the formula can cause errors.
- Compare carefully. Remember, the F-statistic must be greater than the F-critical value to reject the null hypothesis.