This calculator computes the critical values for z, t, F, chi-square, and correlation (r). Simply select the distribution, enter the required parameters, and click the “calculate” button. The calculator will instantly return the correct critical value based on the distribution you select.
Select the distribution, enter the required parameters and click the "calculate" button to get instant results.
How to Use the Critical Value Calculator
This calculator allows you to find the correct critical values without using statistical tables. Here’s how the calculator works:
- Select the distribution (say Z, T, F, Chi-square, or r).
- Enter the required parameters:
- For the z critical values, enter the significance level (α)
- For the critical values, enter the significance level (α) and degrees of freedom (df)
- For the F critical values, enter the significance level (α), numerator degrees of freedom (df1), and denominator degrees of freedom (df2)
- For the chi-square critical values, enter the significance level (α) and degrees of freedom (df)
- For the correlation critical value, enter the significance level (α) and the sample size (n)
- Click the “calculate” button
The calculator will instantly return the critical values you need to make decisions regarding the hypothesis you’re testing.
What is a Critical Value?
A critical value is a cutoff point on a probability distribution (say, normal, F, T) that defines the boundary between the acceptance region and rejection region in hypothesis testing. If the calculated test statistic value falls beyond this cutoff value, you should reject the null hypothesis. Otherwise, do not reject the null hypothesis.
The figure below shows the left, right, and two-tailed critical values along with rejection and acceptance regions.
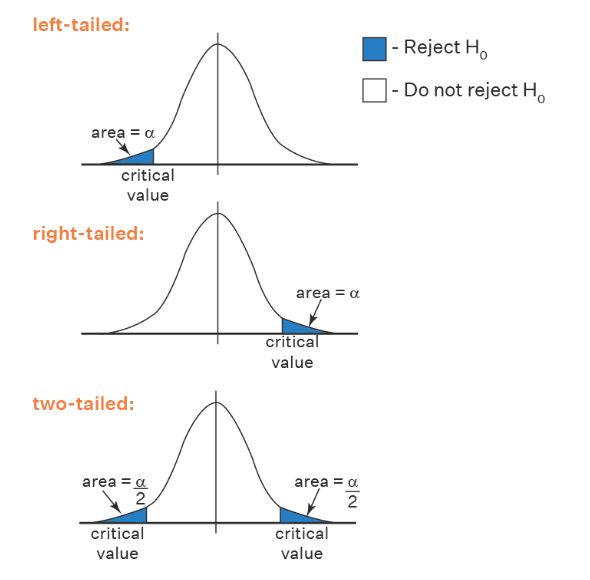
Tip. If the absolute value of the test statistic exceeds (or falls beyond) the absolute critical value, you should reject the null hypothesis and conclude that your result is statistically significant.
What this Calculator Does
Different statistical tests require different distributions. With this one-in-all calculator, you can quickly get critical values for any distribution. Here are the critical values you can get with this tool:
1. Z Critical Value
The z-critical value is ideal when you’re conducting hypothesis tests, or constructing confidence intervals, especially when:
- The population standard deviation is known
- Sample size is large (n ≥ 30)
- Assuming the sampling distribution is normal
While this calculator shows left-tailed, right-tailed, and two-tailed z-critical values, it can be confusing if you’re just looking for z-critical values. In this case, you should consider our critical z value calculator with steps.
2. T Critical Value
We use a t-critical value when testing hypotheses or constructing confidence intervals for t-tests. Thus, it is ideal when:
- The population standard deviation is unknown
- The sample size is small
- Performing t-tests
Since the t-distribution can be left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, this tool will show these critical values. However, if you’re just looking for a quick tool that only provides you with t-critical values, you should use the t-critical value calculator.
3. F Critical Value
The F-critical value is mainly used when you’re conducting a hypothesis for ANOVA tests, comparing two variances, and testing the significance of a regression model. Since the f-distribution is right-skewed, this tool only shows the right-tailed critical value to avoid confusion.
However, if you’re only looking for a quick tool for referencing f-critical values, then you should use the f-critical value calculator.
4. Chi-Square (χ²) Critical Value
When you’re conducting a hypothesis test for the chi-square goodness-of-fit, test of independence, or test of homogeneity, you need to compare the test statistic with the chi-square critical value. This one-in-all calculator also helps you find this value.
However, if you’re only looking for a online tool that specifically gives you χ² critical values, then you should use the custom χ²critical value calculator.
Note. The chi-square distribution is right-skewed. Thus, our tools only show the right-tailed chi-square critical value to avoid confusion.
5. R Critical Value (Correlation)
After running a Pearson’s correlation, you need to use the r critical value to determine whether the correlation is significant or not. This tool also allows you to quickly find the r-critical value for your test.
However, if you’re looking for a tool that only deals with r-critical values and explains the steps, try our r-critical value calculator.
When Should You Use This Combined Calculator?
This all-in-one calculator is ideal when:
- You need a quick answer without a step-by-step explanation
- You’re comparing multiple test types
- You’re reviewing different hypothesis tests
- You want a general-purpose statistical reference tool