This calculator computes the conditional probability of an event occurring given that another has occurred, i.e., P(A/B). It also shows you how to calculate the conditional probability step-by-step.
How to Use the Conditional Probability Calculator
Finding the conditional probability using the calculator is straightforward. Just follow these steps:
- Select the conditional probability you want to calculate
- Enter the joint probability of A and B, P(A ∩ B)
- Enter the probability that Event A or B occurs
- Click the “Calculate” button
The calculator will instantly give you the correct conditional probability based on the type of conditional probability you want to compute. It will also provide you with a step-by-step explanation of how to find the probability manually.
What is Conditional Probability?
In probability theory, conditional probability measures the likelihood of an event happening given that another event has already happened. This means that the two events are dependent since the likelihood of the first happening depends on whether the second event has happened.
The conditional probability formula for an event A happening, given that event B has happened, P(A/B), is given by:
P(A/B) = P(A ∩ B)/P(B)
Similarly, the conditional probability formula for an event B occurring, given that Event A has occurred, P(B/A) is given by:
P(B/A) = P(B ∩ A)/P(A)
In the formula:
- P(A ∩ B) is the joint probability of A and B happening.
- P(A) is the probability that event A will occur
- P(B) is the probability that event B will occur.
Note. P(A ∩ B) is the same as P(B ∩ A) due to the commutative property of probability.
How to Calculate Conditional Probability
To learn how to find the conditional probability of given events, consider the following examples.
Example 1. Conditional Probability Using A Contingency Table
Example 1. A class of 50 students is surveyed about whether they passed a statistics exam and whether they attended revision classes. The following contingency table summarizes the results.
| Passed Exam | Failed Exam | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attended Revision | 30 | 5 | 35 |
| Did Not Attend | 10 | 5 | 15 |
| Total | 40 | 10 | 50 |
If a student is randomly selected from the class, find the probability that the student passed the exam given that they attended revision classes.
By Hand
Let A be the event that the student passed the exam, and B be the event that the student attended the revision class.
Then the probability that the student passed the exam, given that they attended revision classes, can be written as, P(A/B)
By definition, P(A/B) = P(A∩B)/P(B)
From the contingency table:
- The number of students who passed and attended the revision classes is 30
- The number of students who attended the revision classes is 35
Therefore:
- The joint probability of A and B, P(A∩B) = 30/50
- The probability of B, P(B) = 35/50
Hence, P(A/B) = 30/50 ÷35/50
=30/50 * 50/35
=30/35
=0.8571
Therefore, the probability that a student passed the exam given that they attended revision classes is 0.857 (or 85.7%).
Using the Calculator
To calculate the required conditional probability using the online calculator, follow these steps:
Step 1: Identify P(A∩B) and P(B)
From the question:
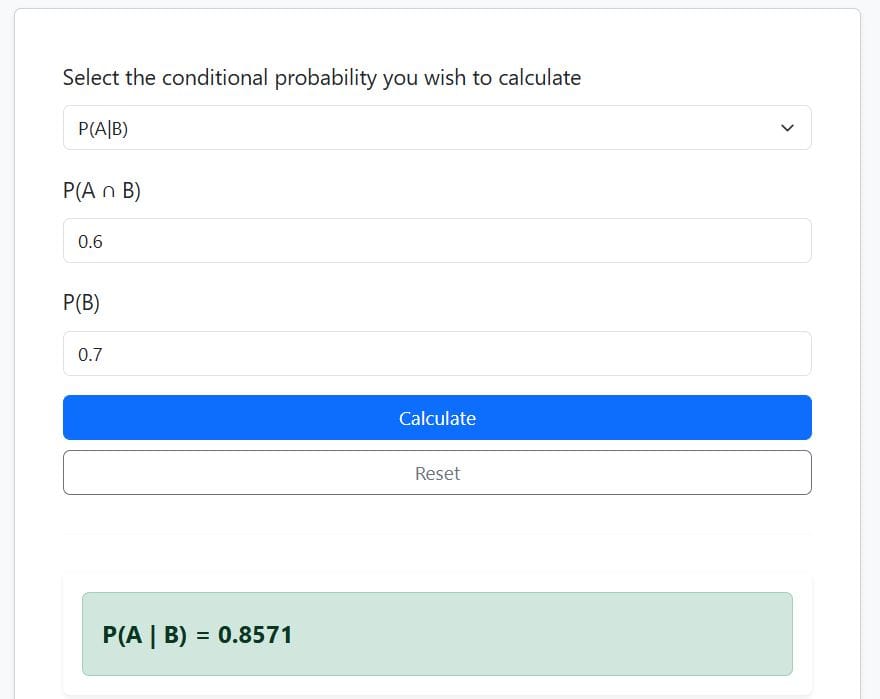
P(A∩B) = 30/50 = 0.6
Also, P(B) = 35/50 = 0.7
Step 2: Select P(A/B) and Enter P(A∩B) = 0.6 and P(B) = 0.7
Step 3: Click the Calculate button
The calculator will instantly return the conditional probability of A, given B, as 0.8571, as shown below
Example 2: Conditional Probability Using Given Probabilities
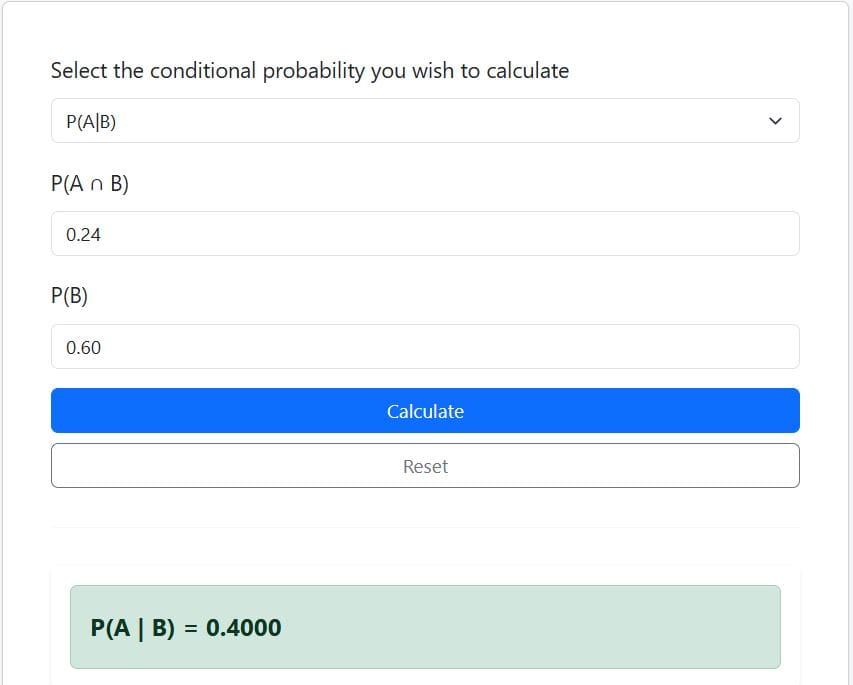
Problem: In a university, 60% of students own a laptop, and 24% of students both own a laptop and use statistical software regularly. If a student is randomly selected, what is the probability that the student uses statistical software regularly, given that they own a laptop?
By Hand
Let A be the event that a student uses statistical software regularly, and let B be the event that a student owns a laptop.
Based on the problem, we know that:
- P(B) = 0.60
- P(A∩B) = 0.24
We need to find P(A/B)
By definition, P(A/B) = P(A∩B)/P(B)
Thus, P(A/B) = 0.24/0.60
=0.40
Therefore, the probability that a student uses statistical software regularly, given that they own a laptop, is 0.40 (or 40%).
Using the Calculator
You can also calculate the required probability using the calculator. You simply need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Identify P(A∩B) and P(B)
From the problem, P(A and B) = 0.24 and P(B) = 0.60
Step 2: Select P(A/B) and insert P(A∩B) = 0.24 and P(B) = 0.60
Step 3: Click the Calculate button
The calculator will instantly return the required probability as 0.40 (see figure below), along with a step-by-step explanation.