The sample mean is the average of a subset of data points collected from a larger population. To calculate the sample mean, you sum all the values in the dataset and divide the results by the number of observations in the sample data. Thus, the sample mean formula is:
x̄ = Σx/n
Where:
- x̄ is the sample mean symbol
- Σx is the sum of all values in the dataset
- n is the number of observations in the dataset
While it is possible to compute the sample mean manually, the process can become complex as you get more data. In such a case, you need to use technologies such as an online sample mean calculator or any other statistical tool, such as Excel or SPSS. In this guide, we’ll teach you how to find the sample mean in Excel using the AVERAGE() function and the manual method.
Finding the sample mean in Excel Using the Average() Function
To find the sample mean in Excel using the Average() function, follow these simple steps:
- Step 1. Enter the data in a single column in Excel
- Step 2. On an empty cell where you want the sample mean to appear, type the formula:
=AVERAGE()and select the cells containing the data. For instance, if the data points are in cells A1:A10, you should type=AVERAGE(A1:A10) - Step 3. Press the “Enter” key on the keyboard to get the sample mean.
Example 1. Calculating Sample Mean in Excel Using the Average() function
Scenario. A lecturer wants to analyze student performance in a statistics exam. The exam scores for a random sample of 20 students are recorded below:
Exam Scores: 89, 92, 44, 56, 78, 71, 79, 92, 65, 68, 74, 78, 78, 64, 60, 58, 43, 46,98, 88
Find the sample mean exam scores using the Average() function in Excel.
Solution
To find the sample mean of the 20 students, follow these steps:
Step 1: Enter the data in Excel by typing it in a single column (A2:A21) as shown below.
Note. A1 contains the data label.
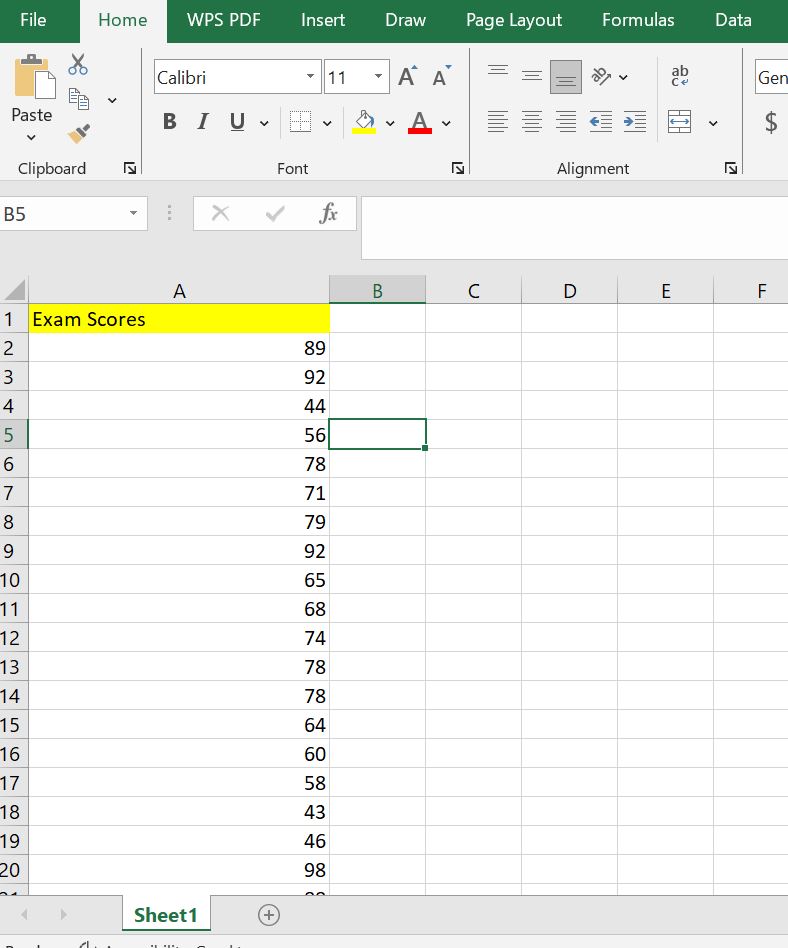
Step 2: On cell B2, type the formula: =AVERAGE(A2:A21).
A2:A21 represents the cell range. In this case, the data points are in cell A2:A21. You can also obtain this by selecting all the cells containing your data.
Step 3: Click the Enter Key on the keyboard to get the sample mean
Combining steps 2 and 3, Excel will return the sample mean of the data as 71.05 (see Figure below)

Finding the sample mean in Excel using the Manual Method
This is the traditional way of finding the sample mean. It involves applying the sample mean formula in Excel, where you first sum all the values in the dataset and divide the results by the number of observations in the dataset.
Therefore, to find the sample mean using the manual method in Excel, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Enter the data in a single column in Excel, say A1:A10
- Step 2: Find the sum of all values in the dataset using the
SUM()function. Assuming the data is in cells A1:A10, then you need to type the formula:=SUM(A1:A10) - Step 3: Find the number of observations in the dataset using the
COUNT()function. If the data is in cells A1:A10, you should type the formula:=COUNT(A1:10) - Step 4: Divide the sum of all values by the number of observations in the dataset to get the sample mean. Thus, the sample mean will be computed by typing the formula:
=SUM(A1:A10)/COUNT(A1:A10)
Example 2: Finding the Sample Mean in Excel using the Manual Method
In some statistics exams and coursework, you may be required to show the manual calculation of the sample mean alongside using Excel functions. In this example, we use the same dataset from Example 1 to demonstrate how to compute the sample mean in Excel step by step using the formula.
Step 1: Enter the data in a single column
The dataset contains 20 observations. So, assuming the first row contains the data label, then the dataset will be contained in cells A2:A21 as shown below:

Step 2: Find the sum of all values in the dataset and store the results in cell C2
In cell C2, type the formula =SUM(A2:A21) to find the sum of all the values in the dataset. The sum of all values will be 1421 as shown below:
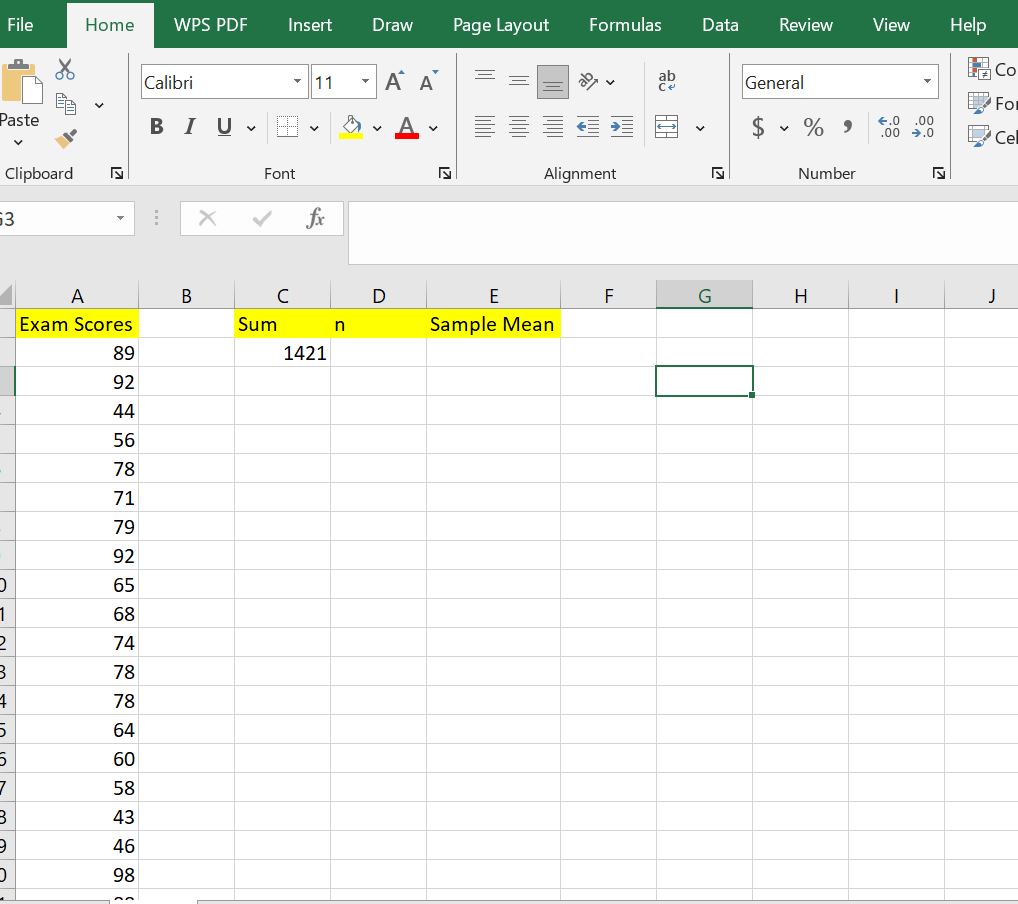
Step 3: Find the number of observations in the dataset and store the results in cell D2
In cell D2, type the formula =COUNT(A2:A21). This will return the sample size as 20, as shown below:
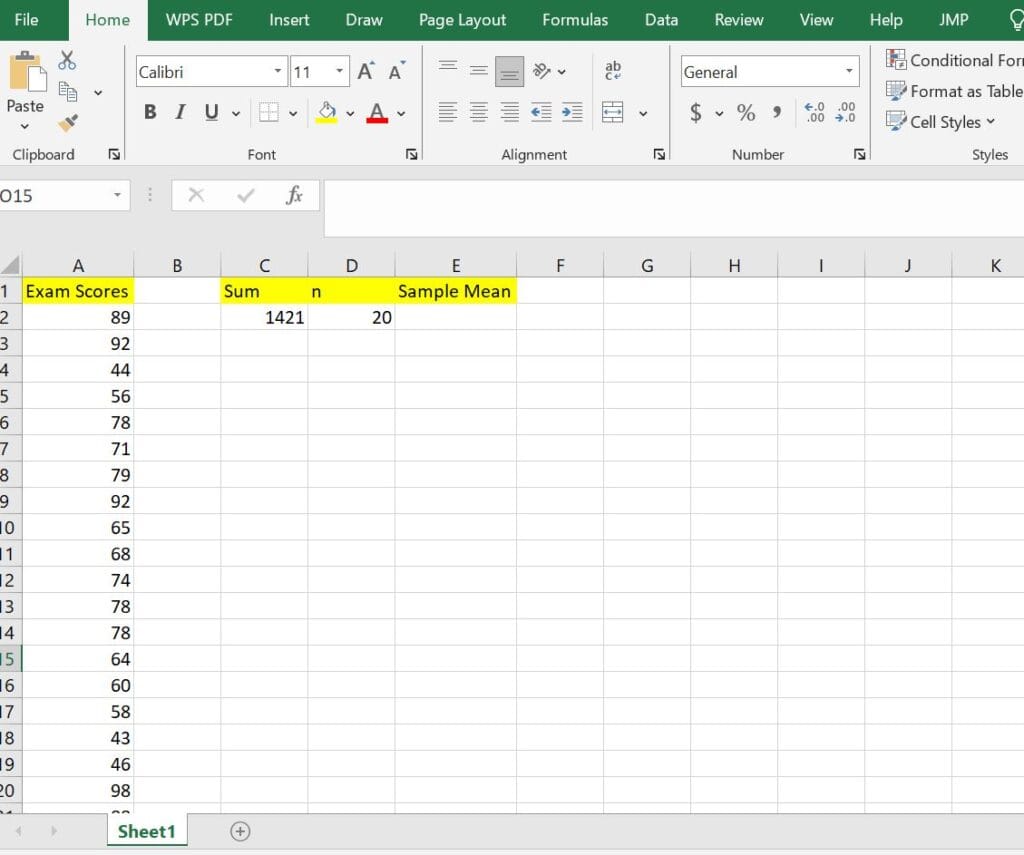
Step 4: Divide the sum of all values by the sample size (n) and store the results in cell E2 to get the sample mean
In cell E2, type the formula =C2/D2. This will give you the sample mean as 71.05, as shown below:
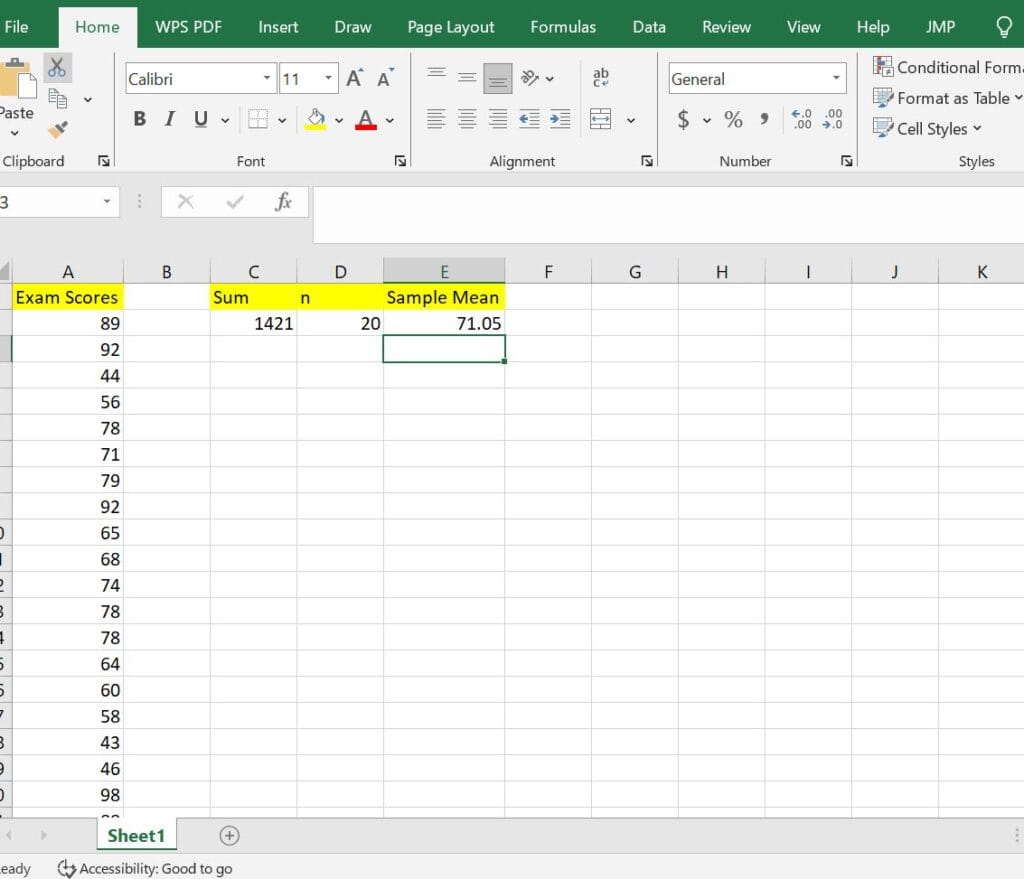
Alternatively, if you don’t want to show all the computations in separate cells, type the combined formula in a cell where you want to store the sample mean and click the Enter Key.
In this case, you would type the formula =SUM(A2:A21)/COUNT(A2:A21) in a cell where you want to store the sample mean results and click the Enter key. Excel will return the sample mean as 71.05, as shown below.

Common Errors to Avoid When Finding the Mean in Excel
As you can see, calculating the sample mean in Excel is straightforward. However, small mistakes can lead to incorrect results. Here are common mistakes students make and how to avoid them.
- Forgetting to select all values. Make sure your formula includes every cell in your dataset. Missing even one value can produce an incorrect mean.
- Blank cells or text entries. Empty cells or text in your range can cause errors such as
#DIV/0!or skew your results. Check your data and remove or correct any non-numeric entries. - Data stored as text. Sometimes numbers are stored as text, especially when copied from another program. Excel will ignore these in calculations. Thus, you should always convert text to numbers using the VALUE function or by reformatting cells.
- Using AVERAGE for filtered data. The
AVERAGEfunction includes hidden rows. If you are working with filtered data, useSUBTOTALorAVERAGEIFto calculate the mean only for visible values.
Frequently Asked Questions
The fastest way is to use the AVERAGE function. Simply type =AVERAGE(range) where your numbers are located, and Excel will return the mean instantly.
Yes, =SUM(range)/COUNT(range) is fully reliable. It’s especially useful if you want to understand or show the calculation step by step, rather than using the built-in function.
Yes, blank cells or cells containing text can cause errors or skew your results. Although functions like AVERAGE can ignore blank cells; you should always correct non-numeric text to avoid errors.
This usually happens when numbers are stored as text, some cells are missing, or the wrong range is selected. Always check your data format and ensure all numeric values are included.
