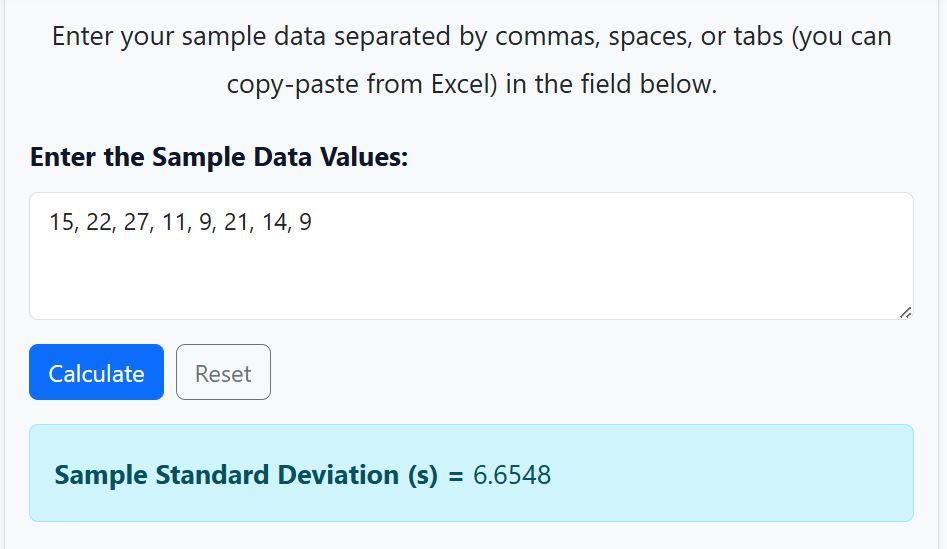
This calculator finds the sample standard deviation once you enter the sample data values. Simply enter the sample data points separated by commas, spaces, line breaks, or copy-paste from Excel and hit the “Calculate” button.
The calculator instantly returns the sample standard deviation, along with a clear step-by-step solution.
Enter your sample data separated by commas, spaces, or tabs (you can copy-paste from Excel) in the field below.
Need to quickly find the population standard deviation? Use the population standard deviation calculator now.
How to Use the Sample Standard Deviation Calculator
Need a quick way to calculate the sample standard deviation? Follow these simple steps for instant results:
- Step 1. Enter sample data values (they can be separated by space, comma, or copy-paste from Excel)
- Step 2. Click the “Calculate” button
The calculator will instantly return the accurate results, with a clear step-by-step explanation. Specifically, the explanation shows you exactly how you can find the sample standard deviation by hand.
What is the Sample Standard Deviation?
The sample standard deviation is a measure of dispersion that quantifies how spread out the sample data is from the sample mean. A small sample standard deviation indicates that the data points are clustered closely around the mean. On the other hand, a large value means that the data is more widely spread.
Sample Standard Deviation Formula
The sample standard deviation formula is:
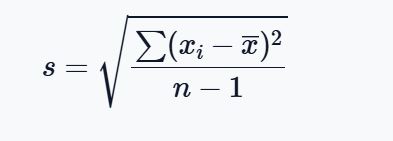
Where:
- s is the sample standard deviation
- xi represents each individual data value
- x̄ is the sample mean
- n is the number of observations in the sample
- ∑(xi−x̄)2 represents the sum of all squared deviations
Note. Because a sample does not perfectly represent the full population, the formula is slightly different from the population standard deviation formula. Specifically, instead of dividing by the sum of squared deviations by n, we divide by n − 1. This adjustment is called Bessel’s correction. It helps reduce bias when estimating the true population variability, hence yielding a more accurate estimate.
Sample vs. Population Standard Deviation
When working with data, one of the most common questions is: Should I use the sample standard deviation or the population standard deviation? The answer depends on the type of data you have.
Here’s how to choose between population vs. sample standard deviation:
- Use population standard deviation if the data is from the entire set of individuals you’re interested in (population)
- Use the sample standard deviation when you’re working with a subset (a sample) drawn from the target population. In most real-world problems, you’ll find yourself working with sample data, hence the sample standard deviation.
The table below shows a summary of the key differences between the sample and population standard deviation.
| Feature | Sample Standard Deviation | Population Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | s | σ |
| Denominator | n − 1 | n |
| Used When | Data is a sample from a larger population | Data includes the entire population |
| Purpose | Estimates population variability | Measures actual population variability |
| Excel Formula | STDEV.S () | STDEV.P () |
How to Calculate the Sample Standard Deviation
Calculating the sample standard deviation manually is easy once you understand the formula. Here are the main steps you should follow:
- Find the Sample Mean
- Subtract the Sample Mean From Each Value and Square the Result
- Sum All the Squared Deviations
- Divide the Sum of Squared Deviations by n−1
- Take the Square Root of the Result
Example
Calculate the Sample Standard Deviation of the following sample data
Dataset: 15, 22, 27, 11, 9, 21, 14, 9
Solution
Step 1. Find the Sample mean
By definition, the sample mean formula is x̄ = ∑xi/n
= (15 + 22 + 27 + 11 + 9 + 21 + 14 + 9)/8
=128/8
= 16
Step 2. Subtract the Sample Mean From Each Value and Square the Result
The results will give us (xi−x̄)2
The table below shows how to subtract and square each deviation
| xi | xi – 16 | ( xi – 16)2 |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | 15-16 = -1 | (-1)2 = 1 |
| 22 | 22-16 = 6 | (6)2 = 36 |
| 27 | 27-16 = 11 | (11)2 = 121 |
| 11 | 11-16 = -5 | (-5)2 = 25 |
| 9 | 9-16 = -7 | (-7)2 = 49 |
| 21 | 21-16 = 5 | (5)2 = 25 |
| 14 | 14-16 = -2 | (-2)2 = 4 |
| 9 | 9-16 = -7 | (-7)2 = 49 |
Step 3. Sum all the Squared Deviations
We need to find the sum of all values in the column, ( xi – 16)2. This will give us the numerator of the sample standard deviation formula, ∑(xi−x̄)2
Thus, ∑(xi−x̄)2 = 1 + 36 + 121 + 25 + 49 + 25 + 4 + 49
=310
Step 4. Divide the sum of squared deviations by n-1
There are 8 observations in the sample data. Thus, n = 8.
Therefore, n-1 = 8-1
= 7
Dividing the sum of squared deviations by n-1 gives: 310/7
=44.2857.
This variance is the sample variance
Step 5. Take the Square root of the results
The sample standard deviation is the square root of its variance.
Thus, the sample standard deviation, s = √(44.2857)
=6.6548
Using our sample standard deviation calculator, we get similar results, as shown below.